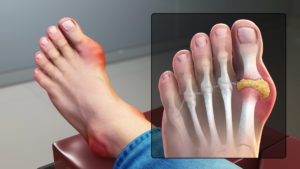
Gout is characterized by sudden, severe attacks of burning pain, redness and tenderness in joints, often the joint at the base of the big toe. These attacks can happen over and over unless gout is treated. Over time, they can harm your joints, tendons, and other tissues.
It is caused by elevated levels of uric acid in the blood. The uric acid crystallizes, and the crystals deposit in joints, tendons, and surrounding tissues.
It is sometimes referred to as the “disease of kings,” because people long have incorrectly linked it to the kind of overindulgence in food and wine only the rich and powerful could afford. In fact, gout can affect anyone, and its risk factors vary.
Men are more likely to get gout, but women become increasingly susceptible to gout after menopause.
The signs and symptoms of gout are almost always acute, occurring suddenly — often at night — and without warning. They include:
- Intense joint pain – Gout usually affects the large joint of your big toe, but it can occur in your feet, ankles, knees, hands and wrists. The pain is likely to be most severe within the first 12 to 24 hours after it begins.
- Lingering discomfort – After the most severe pain subsides, some joint discomfort may last from a few days to a few weeks. Later attacks are likely to last longer and affect more joints.
- Inflammation and redness -The affected joint or joints become swollen, tender and red.
Most patients with gout will experience repeated attacks of arthritis over the years.
Uric acid crystals can deposit in tiny fluid-filled sacs (bursae) around the joints. These urate crystals can incite inflammation in the bursae, leading to pain and swelling around the joints (a condition called bursitis).
In chronic gout, nodular masses of uric acid crystals (tophi) deposit in different soft-tissue areas of the body. Even though they are most commonly found as hard nodules around the fingers, at the tips of the elbows, in the ears, and around the big toe, tophi nodules can appear anywhere in the body. They have been reported in unexpected areas such as in the vocal cords or (rarely) even around the spinal cord.
Hyperuricemia is the underlying cause of gout. This can occur for a number of reasons, including diet, genetic predisposition, or underexcretion of urate, the salts of uric acid.
Normally, uric acid dissolves in your blood and passes through your kidneys into your urine. Renal underexcretion of uric acid is the primary cause of hyperuricemia in about 90% of cases, while overproduction is the cause in less than 10%.
In addition to an inherited abnormality in handling uric acid, other risk factors for developing gout include obesity, excessive weight gain (especially in youth), moderate to heavy alcohol intake, high blood pressure, abnormal kidney function and eating too much meat and fish that are high in chemicals called purines. Some medicines, such as diuretics, can also bring on gout.
In patients at risk of developing gout, certain conditions can precipitate acute attacks of gout. These conditions include dehydration, injury to the joint, fever, excessive eating and recent surgery.
Factors that increase the uric acid level in your body include:
- Diet. Eating a diet rich in meat and seafood and drinking beverages sweetened with fruit sugar (fructose) increase levels of uric acid, which increase your risk of gout. Alcohol consumption, especially of beer, also increases the risk of gout.
- Obesity. If you're overweight, your body produces more uric acid and your kidneys have a more difficult time eliminating uric acid.
- Medical conditions. Certain diseases and conditions increase your risk of gout. These include untreated high blood pressure and chronic conditions such as diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and heart and kidney diseases.
- Certain medications. The use of thiazide diuretics — commonly used to treat hypertension — and low-dose aspirin also can increase uric acid levels. So can the use of anti-rejection drugs prescribed for people who have undergone an organ transplant.
- Family history of gout. If other members of your family have had gout, you're more likely to develop the disease.
- Age and sex. Gout occurs more often in men, primarily because women tend to have lower uric acid levels. After menopause, however, women's uric acid levels approach those of men. Men are also more likely to develop gout earlier — usually between the ages of 30 and 50 — whereas women generally develop signs and symptoms after menopause.
- Recent surgery or trauma. Experiencing recent surgery or trauma has been associated with an increased risk of developing a gout attack.
The most reliable test for gout is finding uric acid crystals in a sample of the joint fluid obtained by joint aspiration.
Blood uria is the commonest blood test to estimate the level of Uric acid. Other blood tests commonly performed are white blood cell count, electrolytes, renal function, and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR).
X-rays can sometimes be helpful and may show tophi-crystal deposits and bone damage as a result of repeated bouts of inflammation.
Ayurveda Management of Gout

Several causes are listed in Ayurveda, which causes Vatarakta are excessive intake of Lavana (salty), Amla (Sour), Katu (pungent), Tikta (bitter), Kshara (alkaline), Snigdha (Too oily), and Ushna (Too hot) foods, eating dried & preserved or spoiled fish/meat, Ulavalu (Horsegram), Blackgram, Nishpava (anumulu, a bean variety), sour curd or buttermilk, incompatible foods like fish with milk products, drinking alcohol, daytime sleep, staying awake in the night, anger etc.
Based on the seat of the disease, Vatarakta is classified into 2 types.
- Uttana (superficial) – This is located in the twak (skin) & mamsa (muscle).
- Gambhira (deep) – This is located in the deeper dhatus and more severe in nature. Tophi or nodule formation occurs.
At CHARAKA, our treatment includes Ayurveda Panchakarma therapy along with internal medicines, diet & lifestyle modifications. Therapies like Snehapanam, Virechanam, Abhyanga swedam, Elakkizhi, Pizhichil, Vasti, Navarakizhi etc are very useful in treating or even curing Vatarakta.
In very severe cases, even Rakthamokshana therapy is also practiced for quicker and long lasting relief.

